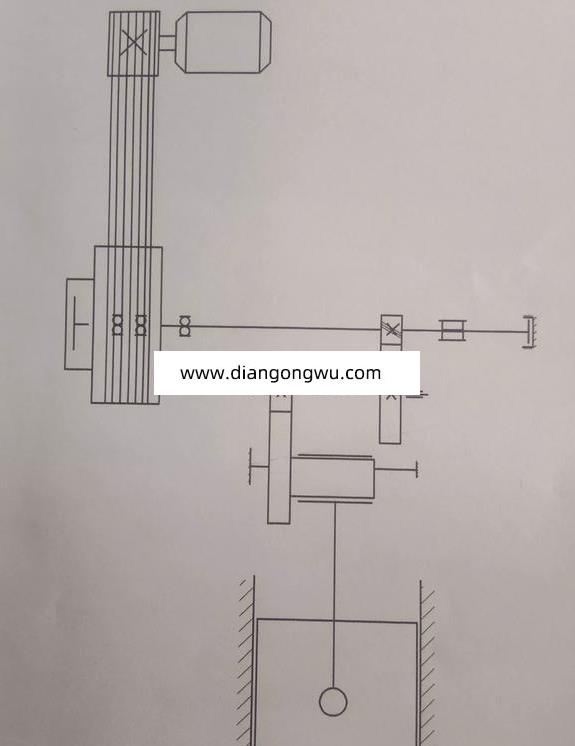
一个纯硬件数字电子时钟的电路图
纯数字电路的时钟,。我有的 。74LS161.555等芯片组成
时间可调
PROTUES仿真
需要去我百度空间看看
最好QQ我
谁数字电子钟的电路图
http://www.wsjx.zjwu.net/d/class/1081035-2090206/web/zonghe/6.htm
实验仪器、工具:
1. 5V电源(或实验箱)4个人合用1个。
2. 四连面包板1块。
3. 示波器2个(每班)
4. 万用表5个(每班)。
5. 镊子1把。
6. 剪刀1把。
六、实验器件
1. 网络线2米/人。
2. 共阴八段数码管6个。
3. CD4511集成块6块。
4. CD4060集成块1块。
5. 74HC390集成块3块。
6. 74HC51集成块1块。
7. 74HC00集成块4块。
8. 74HC30集成块1块。
9. 10MΩ电阻5个。
10. 500Ω电阻14个。
11. 30p电容2个。
12. 32.768k时钟晶体1个。
13. 蜂鸣器10个(每班)
七、设计过程的日程安排
6月28日
1. 分发仪器、工具、器件
2. 讲解总体设计的过程,明确数字钟实现的功能,由哪些相对独立的功能模块组成,各个模块之间互相联系,时钟信号传输路径、方向和频率变化。
3. 讲解面包板的结构和使用方法,连接导线的要点,包括导线剥线头、插线方法、要求,检查面包板,如面包板中的导电铜片变形或移位,更换导电铜片。
4. 七段数码引脚排列测试,验证每段显示为一个发光二极管,同时完成对每个数码管的检查。
6月29日~7月2日
分功能讲解各个模块功能实现原理、实现,搭建实际电路一个个验证。在接线时注意合理布线和接线的可靠性。
6月29日
a) 数码管的译码驱动电路接线、测试、译码器控制功能测试(手工输入测试电平)。
除了进一步熟悉原理外,主要练习接线合理布局,走线整齐、美观,用手指触动导线时也能正常工作。可以静态显示学号的后几位。然选一个可正常工作的译码、显示电路,分别测试译码器的3个控制引脚的作用。
6月30日
b) 晶体震荡电路接线、测试(用示波器测量4060输入时钟,每一路分频输出的频率)。
c) 5进制计数器接线,输入用4060的2Hz,输出用数码管显示。
7月1日
d) 10进制计数器接线、测试。
e) 6进制计数器接线、测试(在10进制基础上改)。
7月2日
f) 60进制计数器接线、测试。
g) 24进制计数器、测试(在60进制基础上改)。
h) 校时电路接线(用RS触发器实现锁定、防抖动功能),用示波器观察电路的信号选择功能。
7月5~7日
5. 在熟悉各个功能模块基础上,结合对总体框图的理解,设计总接线图。
6. 根据总接线图中各种元器件数量、连线,确定所有元器件布局。
7. 按以下顺序接线:晶体震荡、秒电路、分电路、时电路。
8. 如时间允许加接校时电路和报时电路(整点报时)。
7月8~9日
9. 写课程设计报告。
a) 设计的目的、要求。
b) 总体框图设计。
c) 功能模块设计(对所用元器件使用作一些说明)。
d) 总电路图设计。
e) 总结:遇到的问题和解决办法、体会、意见、建议等。
参考资料:http://www.wsjx.zjwu.net/d/class/1081035-2090206/web/zonghe/6.htm

多功能数字钟电路图
数字钟的VHDL设计
1、设计任务及要求:
设计任务:设计一台能显示时、分、秒的数字钟。具体要求如下:
由实验箱上的时钟信号经分频产生秒脉冲;
计时计数器用24进制计时电路;
可手动校时,能分别进行时、分的校正;
整点报时;
2 程序代码及相应波形
Second1(秒计数 6进制和10进制)
Library ieee;
Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Entity second1 is
Port( clks,clr:in std_logic;
Secs,Secg: out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
cout1:out std_logic);
End second1;
Architecture a of second1 is
Begin
Process(clks,clr)
variable ss,sg: std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
variable co: std_logic;
Begin
If clr='1' then ss:=0000; sg:=0000;
Elsif clks'event and clks='1' then
if ss=0101 and sg=1001 then ss:=0000; sg:=0000;co:='1';
elsif sg<1001 then sg:=sg+1;co:='0';
elsif sg=1001 then sg:=0000;ss:=ss+1;co:='0';
end if;
end if;
cout1<=co;
Secs<=ss;
Secg<=sg;
end process;
End a;
Min1(分计数器 6进制和10进制 alm实现整点报时)
Library ieee;
Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Entity min1 is
Port(clkm,clr:in std_logic;
mins,ming:buffer std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
enmin,alarm: out std_logic);
End;
Architecture a of min1 is
Begin
Process(clkm,clr)
variable ms,mg :std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
variable so,alm :std_logic;
Begin
If clr='1' then ms:=0000; mg:=0000;
Elsif clkm'event and clkm='1' then
if ms=0101 and mg=1001 then ms:=0000;mg:=0000; so :='1'; alm:='1';
elsif mg<1001 then mg:=mg+1; so :='0';alm:='0';
elsif mg=1001 then mg:=0000;ms:=ms+1; so :='0';alm:='0';
end if;
end if;
alarm<=alm;
enmin<= so;
mins<=ms;
ming<=mg;
End process;
End a;
Hour1(时计数器 4进制与2进制)
Library ieee;
Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Entity hour1 is
Port(clkh,clr:in std_logic;
hours,hourg:out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0));
End;
Architecture a of hour1 is
Begin
Process(clkh,clr)
variable hs,hg :std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
Begin
If clr='1' then hs:=0000; hg:=0000;
Elsif clkh'event and clkh='1' then
if hs=0010and hg=0011 then hs:=0000;hg:=0000;
elsif hg<1001 then hg:=hg+1;
elsif hg=1001 then hg:=0000;hs:=hs+1; end if;
end if;
hours<=hs;
hourg<=hg;
End process;
End;
Madapt(校分)
Library ieee;
Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Entity madapt is
Port(en,clk,secin,m1:in std_logic;
minset:out std_logic);
End;
Architecture a of madapt is
Begin
Process(en,m1)
Begin
if en='1' then
if m1='1' then minset<=clk;
else minset<=secin; end if;
else minset<=secin ;
end if;
End process;
end;
Hadapt (校时)
Library ieee;
Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Entity hadapt is
Port(en,clk,minin,h1:in std_logic;
hourset:out std_logic);
End;
Architecture a of hadapt is
Begin
Process(en,h1)
Begin
if en='1' then
if h1='1' then hourset<=clk;
else hourset<=minin; end if;
else hourset<=minin;
end if;
End process;
end;
Topclock(元件例化 顶层文件)
Library ieee;
Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_arith.all;
Use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Entity topclock is
Port(clk,clr,en,m1,h1:in std_logic;
alarm:out std_logic;
secs,secg,mins,ming,hours,hourg:buffer std_logic_vector(3 downto 0));
End;
Architecture one of topclock is
Component second1
Port( clks,clr:in std_logic;
secs,secg: buffer std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
cout1: out std_logic);
End Component;
Component min1
Port(clkm,clr:in std_logic;
mins,ming:buffer std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
enmin,alarm: out std_logic);
End Component;
Component hour1
Port(clkh,clr:in std_logic;
hours,hourg:buffer std_logic_vector(3 downto 0));
End Component;
Component madapt
Port(en,m1,clk,secin:in std_logic;
minset:out std_logic);
End Component;
Component hadapt
Port(en,h1,clk,minin:in std_logic;
hourset:out std_logic);
End Component;
signal a,b,c,d: std_logic;
begin
u1:second1 port map(clr=>clr,
secs=>secs,secg=>secg,clks=>clk, cout1=>a);
u2:min1 port map(clr=>clr,alarm=>alarm,
mins=>mins,ming=>ming,clkm=>b,enmin=>c);
u3:hour1 port map(clr=>clr,
hours=>hours,hourg=>hourg,clkh=>d);
u4:madapt port map(en=>en,m1=>m1,clk=>clk,secin=>a,minset=>b);
u5:hadapt port map(en=>en,h1=>h1,clk=>clk,minin=>c,hourset=>d);
end;
3 电路图
4 实验心得
程序全部都给你写好了啊,只 要你自己仿真,再下载到实验箱就OK了啦
电工电子技术课设,数字电子钟逻辑电路图
其实就是32768HZ的震荡电路和后面的不同倍数的分频电路,再加驱动LED数码管的电路。具体是先分频到1HZ,即得到秒脉冲,再1/60分频,得到分钟,再1/60分频,得到小时。用数字 电路搭比较复杂,但最能检验你的数电水平。用单片机做,电路简单,主要靠程序代码来实现。
数字电子时钟电路图修改助
这个电路改进的希望不太大,毕竟这是数字电路搭建起来的时钟显示模块。
CD4511作为数码管译码电路,电阻是限流的。cd4518和74ls163差不多,用来计数的。
ne555作为时钟模块必不可少,周边期间是它工作的基础。
cd4011作为与门,作为进位控制。
模拟电路快忘光了。数字部分只要知道IC的参数,用法就行。
数字电子时钟电路图修改助、数字钟电路图,就介绍到这里啦!感谢大家的阅读!希望能够对大家有所帮助!